DECOMPOSE AND RELEASE works in two ways: it activates biological processes in the soil, thereby intensifying the decomposition of organic matter, and transforms complex and insoluble forms of phosphorus, such as calcium phosphate, into easily digestible forms, increasing the availability of this element for plants. The product is based on specially selected bacteria of the Bacillus sp. genus and additional ingredients that have a beneficial effect on the activity of microorganisms that accelerate the mineralization of organic matter.
Phosphorus (P), as one of the three essential macroelements, which is also very poorly absorbable, is crucial for plant growth and stimulating root development, enhancing nutrients and water uptake, as well as stabilizing the plant in the substrate. It has a particularly positive effect on the proper course of photosynthesis and other energy processes taking place in plants, as well as the resistance of plants to unfavorable conditions in fields. As a result of phosphorus deficiency, plants significantly slow down their growth rate and become darker. Long-term deficiency of this component in plants causes them to undergrow and have a poorly developed root system.
Phosphorus is needed by plants from the seedling stage to full maturity, but plants absorb it only in the form of hydrogen phosphate ions H2PO4– and HPO42, and the soil itself is not rich in this macronutrient. The concentration of phosphorus in the soil is in the range of 500-800 mg/kg of dry soil, and its average content is 0.05% (w/w). Approximately 60% of soils in Poland are characterized by low or very low content of phosphorus available to plants, and this form constitutes on average only 0.1% of all phosphorus in the soil. Research carried out as part of the “Monitoring the chemistry of Polish arable soils” programme showed that the content of available phosphorus has decreased over several years and its average content expressed as phosphorus pentoxide is 14.65 mg P2O5·100g-1. The factors that influence the absorption of this element are the soil reaction, the content of iron and aluminum compounds, the presence of available calcium and the content of organic substance. The largest amount of it is found in the subsurface layers of soil, and it decreases with the depth of the soil profile. Attention is increasingly paid to the activation of natural mechanisms that increase the bioavailability of phosphorus present in the soil (native and retrograde) due to the fact that a much larger amount of this macronutrient occurs in forms unavailable to plants, and the important role of bacteria in these processes.
The bacteria contained in DECOMPOSE AND RELEASE from the Bacillus sp. genus are known as phosphorus bacteria that transform phosphorus compounds from forms that are inaccessible, and therefore blocked for plants, to forms that are available to them. They secrete enzymes into the soil i.e. phosphatases and phytases, which hydrolyze and mineralize organic compounds. The enzymatic activity of bacteria leads to the transformation of organic phosphorus into inorganic phosphorus, which is available to plants in ionic form. Phosphorus bacteria additionally introduce many substances into the soil that promote plant growth, such as siderophores, auxins, cytokines and vitamins.
The effectiveness of the DECOMPOSE AND RELEASE product in accelerating the decomposition of crop residues and increasing the amount of phosphorus available to plants, as a result of the action of the bacteria contained in it, is confirmed by tests performed in our test laboratory.
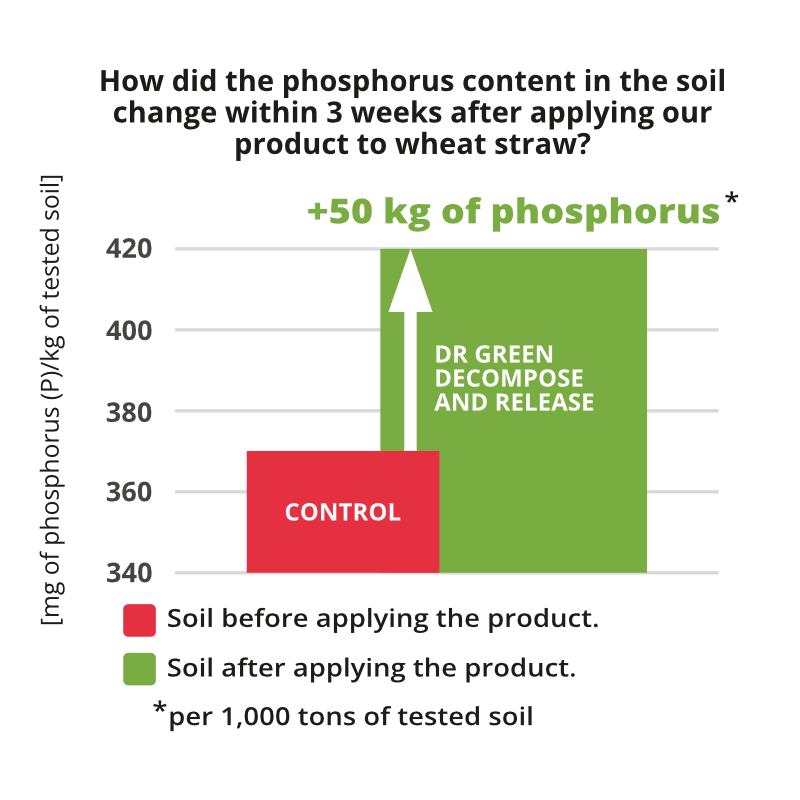
Field conditions were reproduced in a phytotron chamber and an analysis of the phosphorus content in the soil was performed before and after application of the formulation at a dose of 2 kg/ha/200l after three weeks.
| How did the phosphorus content in the soil change within 3 weeks after applying our formulation to wheat straw? | ||
|---|---|---|
| | Phosphorus (P) [mg/kg] | Phosphorus pentoxide (P2O5) [mg/kg] |
| SOIL BEFORE APPLICATION OF THE FORMULATION | 370 | 850 |
| SOIL AFTER APPLICATION OF THE FORMULATION | 420 | 960 |